Plant sterols – What are they? Where are they found? Duncan Farrington, founder of Farrington Oils, explains.
Many health-related issues are a direct result of poor diets, especially Coronary Heart Disease, which is a major killer in westernised populations. One of the biggest causes of Coronary Heart Disease is from high cholesterol. Raised cholesterol levels are partly genetic, but also partly a result of poor dietary choices. By eating a healthy balanced diet, over time you can bring your cholesterol levels back to your normal level.
In recent years, interest has increased in a particular natural food component that actively reduces cholesterol, called plant sterols. Plant sterols are fat-soluble compounds found in some vegetables, nuts and seeds, including rapeseed. They are similar in structure to cholesterol, which is found in animal fats such as meat and dairy. When eaten, plant sterols compete with cholesterol for absorption into the bloodstream. Your body finds it easier to absorb the plant sterols: they block the cholesterol from being absorbed, resulting in the cholesterol passing through and out of the body via the stool.
Plant sterols’ cholesterol-lowering effects have been known for some time. They are considered to be the most effective single food that can lower cholesterol as part of a healthy diet and lifestyle. Evidence suggests that eating between 1.5g and 2.4g of plant sterols each day can significantly reduce LDL cholesterol (‘bad’ cholesterol) by up to 10% (Heart UK).
These beneficial plant sterols are present in rapeseed oil. In fact, several vegetable oils contain plant sterols, with rapeseed oil being an excellent source, as shown in the table. Rapeseed oil has over double the sterol content of olive oil, and ten times that of coconut oil.
Total sterol content of crude vegetable oils.
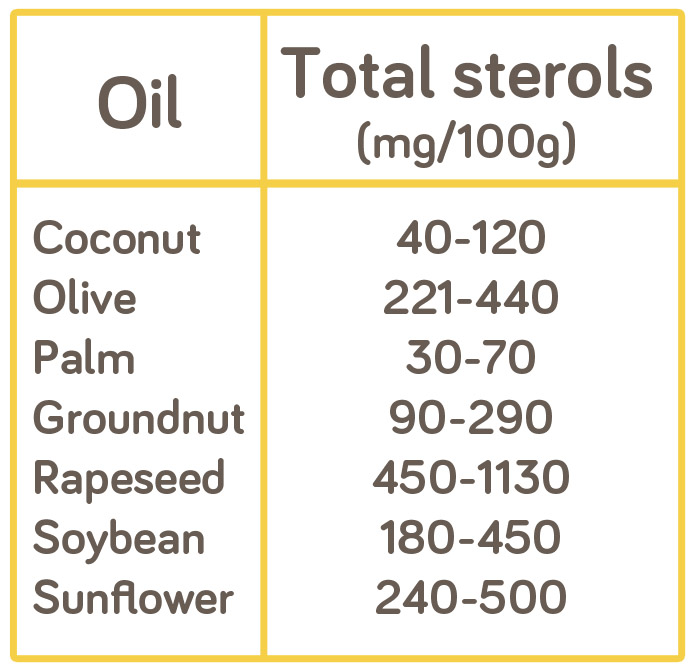
Adapted from Gunstone (2004) and Gunstone (2011).
As you can see, rapeseed oil contains the highest amount of plant sterols. This table is for crude oils, which means it is based on unrefined oils such as a cold pressed rapeseed oil. If we look at the refined versions of these oils, the plant sterol measurement decreases by up to 40%. This is caused by the bleaching and deodorising process. So, in order to consume more plant sterols from oils, an unrefined and cold pressed rapeseed oil, such as Farrington’s Mellow Yellow, is the best choice.
The knowledge of how effective plant sterols are in lowering cholesterol has led to the appearance of several successful food brands producing fortified foods, such as non-dairy spreads and yoghurt drinks with ‘added plant sterols’. The plant sterols added are actually those recovered from refined vegetable oils.
Although our rapeseed oil contains high amounts of plant sterols in comparison to other oils, I am not suggesting that Farrington’s Mellow Yellow alone will reduce cholesterol levels. To get your full 1.5g to 2.4g of plant sterols a day, you would need to drink around half a bottle of cold pressed rapeseed oil, which is obviously not realistic, nor how I suggest you enjoy our oil! However, by enjoying it alongside other plant sterol containing foods, as part of a healthy diet, you’ll increase your total plant sterol intake and be well on your way to reaching the ideal amount needed to reduce high cholesterol.
Duncan Farrington
For more information on this topic, see:
Gunstone F D., (2004). Rapeseed and Canola Oil; Productrion, Processing, Properties and Uses Blackwell Publishing
Gunstone F D., (2011). Vegetable Oils in Food Technology Composition, Properties and Uses Wiley-Blackwell p253-254.
Heart UK. https://heartuk.org.uk

 Oils
Oils Rapeseed Oil
Rapeseed Oil Chili Oil
Chili Oil Dressings
Dressings Blackberry Vinaigrette
Blackberry Vinaigrette Classic Vinaigrette
Classic Vinaigrette Balsamic Dressing
Balsamic Dressing Honey & Mustard
Honey & Mustard Ultimate Chilli Dressing
Ultimate Chilli Dressing