Our team headed to the Weetabix Northamptonshire Food & Drink Awards last week—an annual event that celebrates local food and drink suppliers, growers, and producers in Northampton. It was wonderful to be in a room with other like-minded folks, all striving for the same thing: to ensure the food we grow and create in the county is not just delicious and high in quality but also sustainable, ethical, and beneficial to everyone along the production line.
The Farming Environment Award is sponsored by Weetabix and recognises protocol growers who have supplied Weetabix within the last two years. It looks at growers who have taken meaningful steps to reduce the environmental impact of wheat growing, whilst taking measurable actions to reduce carbon footprint, promote biodiversity and practice regenerative agriculture.
We are so proud of our farm’s sustainable credentials and our ongoing work to promote biodiversity, so when Farrington’s Farm was announced as the winner of the GOLD award, we were naturally delighted! Of course, it’s always wonderful to win an award, but when it recognises the work, time, effort, and collaborative journey our team has been on to nurture our land and help it thrive, it is even more special.
Here are some of the reasons that led to our award win:-
– We are committed to regenerative agriculture and environmental preservation. And we are always looking at ways in which we can nurture our soil to ensure all of our crops, from wheat to make Britain’s favourite breakfast cereal, to rapeseed which we press on site to make Mellow Yellow cold pressed rapeseed oil is the absolute best it can be.
– We are a LEAF Marque accredited producer and a LEAF demonstration farm. This means we have been independently verified under LEAF’s robust sustainability credentials.
– We stopped ploughing in 1998 and practice minimum and zero tillage to establish crops. Allowing worms and other little soil beasties to create a healthy soil full of life to help us grow our crops.
– To date, around 6,000 trees and over 8km of hedges have been planted, along with extensive wildlife habits created, improved, and maintained around the farm.
– Our farm was certified Carbon Neutral in 2020.
– A network of over 8km of well-maintained public rights of way invites people to enjoy the countryside.
Find out more about our approach to sustainability and our credentials.
Every year at the start of August, farmers are encouraged to share their day online as part of 24 Hours in Farming #Farm24. We took part again this year and shared all the goings on from Bottom Farm.
First, we headed out to find Marvin cultivating. This field was growing wheat this year which has now been harvested, we leave the wheat stubble in the field to biodegrade and nourish the soil. We are planning on planting beans in this field in October and beans need to be planted quite deep into the ground. Marvin has to cultivate the soil to loosen the top layer to make it possible for us to plant the beans. This is a big field and the cultivator needs to be driven quite slowly so this will take the majority of the day!

We then headed back to the farm yard, passing the combine harvester which is having a rest until the spring barley is ready to be harvested.
![]()

Here are the wild flowers we have growing around our spring barley. These flowers provide habitats for insects and is great for pollinators.

We even have these beautiful daisies in the wildflower meadow margins, and Duncan explained these are actually chamomile for making into tea!

The last stop on our way back to the farmyard was these trees. Duncan planted them back in 1989 and they are just a few of the 8000 trees he has planted on the farm over the years.

Heading into our rapeseed oil production area, we watched the team pressing and bottling our Mellow Yellow Rapeseed Oil. We cold press our rapeseed on our farm. Our presses run 24/7 to produce Mellow Yellow Rapeseed Oil for kitchens up and down the country! We call it the process of no process. Simply sow, grow, press and bottle!

We harvested our rapeseed a few weeks ago and this what the little seeds look like. They’re bright yellow inside and packed full of delicious and nutritious oil!

After lunch, Duncan headed out to do some mowing. Tidying up the edges of fields already combined and making sure the various public footpaths we have going through the farm are clear and accessible for people on their daily walks!

Before we harvest the wheat, we need to check the moisture content, still a few more days of sunshine needed for this field! Duncan is winnowing here – blowing air through the wheat to remove the chaff!

We then left Marvin finishing off the cultivating and that was our day!

We had a great time sharing our day on the farm and we hope you enjoyed getting an insight into British farming! See you next year!
Soil health is a big part of sustainable farming and I have been measuring this on one of my fields since 2002. Among the great soil nutrition and health improvements seen in this field due to my sustainable farming practices, I have farmed in a way that has increased soil organic matter (SOM) which has a direct impact on reducing atmospheric CO2 levels. Between 2002 and 2020 I have seen my SOM increase from 3.8% to 6.7% which is a significant amount when talking about soil!
What is Soil Organic Matter?
Soil organic matter is the organic part of soils consisting of plant and animal detritus at various stages of decomposition. Think of dead leaves off trees, straw left behind after crops have been harvested, decaying soil microbes and insects, or old plant roots in the soil.
The organic matter is made up of cells and molecules containing lots of carbon and it can be lost from soils over the years through natural processes, which is sped up if soils are moved intensively, mixing with oxygen in the atmosphere and released as carbon dioxide (CO2). Commonly this occurs when a field is ploughed.
We no longer plough our fields and have worked hard on our sustainable farming methods to keep the carbon in the soil. In the right conditions SOM can be increased over the years, as plants grow, taking carbon dioxide out of the atmosphere to create plant material through the natural process of photosynthesis. The process of taking CO2 out of the atmosphere and storing in the soil is called carbon sequestration and the soil becomes a carbon sink as it reduces the levels of CO2 in the atmosphere.
Soils have the ability to be fantastic carbon sinks when looked after. In fact, coal and mineral oils that are mined from the ground (fossil fuels) are carbon that has been stored from hundreds of millions of years ago, formed from decayed plants and animals that once grew and roamed the earth.

How does this relate to our farm?
On my field called ‘Below the Black Barn’ the increase in soil organic matter has removed CO2 from the atmosphere, locking it in the ground which is great for reducing global warming as well as making the soil more nutritious for the plants to grow in. The figures are very impressive. We know that for every 0.1% increase in SOM, around 8.9 tonnes of CO2 are sequestered on every hectare of land.
But what does this actually mean?
If my field has increased the total SOM by 2.9% over 18 years, it has absorbed around 258 tonnes of CO2 per hectare (ha), or 14.34 tonnes per ha per year on average. One hectare is around the same size as one and a quarter football pitches.
To put this into context, driving a 1.5lt petrol Mini (our Mellow Yellow Mini) car produces 117g of CO2 per Km. So, for every hectare of our field we are absorbing enough CO2 to off-set nearly 122,554km of motoring, which is equivalent to over 10 years driving for the average motorist!
Let’s look at the whole farm…
This is just off one hectare, but Below the Black Barn Field has a cropped area of around 20ha and our whole farm cropped area is around 272ha. Therefore, from the way we farm our soils, we are sequestering an impressive 3900 tonnes of CO2 per year, off-setting enough CO2 to fly one person 500 times around the world in economy class! (or take 2,778 cars off the road) each year.

The story does not end with the cropped area
We have a medium sized family farm, which not only includes the cropped area, but all the other bits we do around the edges of our fields as part of our LEAF farming and sustainable farming practises. These include areas of woodland and hedges, a grass meadow, areas of native wild-flowers and grass margins. Over the years we have planted well over 8,000 metres of new hedges and over 8,000 native trees on the farm to add to the existing trees and hedges. All these conservation areas can be calculated to sequester a further 240 tonnes of CO2 per year, as well as being areas for wildlife to thrive and prosper.
In summary on our medium sized family farm in Northamptonshire, following our LEAF and sustainable farming principles of a common-sense approach to sustainable agriculture and soil management, we are absorbing over 4,100 tonnes of CO2 per year, which is equivalent to an awful lot of car journeys or air miles. If all farmers around the world were to farm in a similar manner, there is the potential to offset all the global carbon emissions created by global transport, which is about 30% of the carbon dioxide emitted. Or another way of looking at it, by increasing soil organic matter content from 1.7% to 5.2% on agricultural land globally, would take 1 trillion tons (0.9 trillion tonnes) of carbon dioxide out of the atmosphere, bringing it down to pre-industrial levels.
The good news is that we are not the only people practicing some fantastic sustainable farming techniques growing quality crops, livestock and wildlife habitats on our farm. As well as pressing rapeseed grown on our farm, we buy seed off four other LEAF Marque farmers who are just as passionate as we are in the way they farm. So, between us we are all doing our bit to preserve and protect the planet for future generations.
Further reading, in no particular order:
Montgomery. D.A, 2017. Growing a Revolution, Bringing our soil back to life. (Available from Amazon here.)
www.indigoag.com/the-terraton-challenge
www.co2.myclimate.org/en/flight_calculators/new
www.soilquality.org.au/factsheets/organic-carbon
On a very wet Sunday in February, with Storm Dennis doing his best to ruin the weekend, we were joined by 30 local volunteers in waterproofs and wellies to tackle climate change head on for our tree planting day.
Trees are the lungs of our planet, they absorb carbon, fight flooding, reduce pollution, nurture wildlife and enhance the beautiful English countryside. Since 1987, we have planted over 8,000 trees on the farm and this time, we thought we would ask the local community for their help with our next tree planting effort.

With the support of The Woodland Trust, we were advised to choose trees that suited the wet conditions of the area the trees would be planted in. They suggested hawthorn, crab apple, hazel, goat willow and holly, which will grow to create a wild wood area. We bought the trees from The Woodland Trust, they sell small saplings that are UK sourced and grown to help prevent the spread of trees diseases and pests. By buying trees from The Woodland Trust, it helps support the fantastic work they do in protecting, restoring and creating the UK’s woodlands. To buy your own trees from The Woodland Trust, visit their shop here.


To start the day off, all our volunteers gathered in our grain store and were served delicious tea and coffee from local coffee roastery, No. 13 Coffee. They roast their own beans in nearby Kettering and then serve their coffee from a converted horse box, which is solar powered! Eli Farrington made a wonderful selection of cakes, all using Mellow Yellow Rapeseed Oil. With everyone settled with a hot drink and slice of cake, Duncan explained why planting trees is so important and the correct tree planting technique. Then it was time to head out into the rain. Armed with spades and umbrellas, we handed out the saplings and our trusty volunteers got digging!
By the time all the trees were in the ground, everyone was pretty wet and cold, so we went straight back to the grain store to enjoy another hot drink from No. 13 Coffee and another slice of cake, after all, we had earned it!

The weather didn’t dampen anyone’s spirits and we hope all our volunteers had a nice time. Trees absorb carbon dioxide all their life, but are most efficient during their teenage to middle age years. So for the next few years, these trees will focus on growing and then in about 10 years, will start really making a difference to global atmospheric carbon dioxide levels. Planting trees is a true investment for the future of our planet, so we are incredibly grateful for all our volunteers and the help they provided! If you want to learn more about why planting trees is so important, have a read of this blog post.
If you want to plant your own trees or attend a tree planting day, visit The Woodland Trust’s website.
What is carbon sequestration?
“Carbon sequestration is the long-term removal of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere to be stored in plants, soils, geologic formations or oceans.”
This sentence very simply defines what carbon sequestration is, but I will explain a bit more about what it actually means and how soils and sustainable farming practices can have a major impact on reducing global warming by reducing the carbon dioxide (CO2) levels in the atmosphere.
Soil carbon sequestration is a natural process powered by growing plants, through the process of photosynthesis. Plants photosynthesise with the energy from sunlight, taking CO2 out of the atmosphere and converting this into new plant material, both above and below the soil surface, locking up the carbon and releasing the oxygen back to the atmosphere. The process works in symbiosis with the minerals, water, bacteria, fungi and other organisms in the soil. Plants grow, die and decay, feeding the soil and the life within it. Over the long term, CO2 is removed from the atmosphere, locked into the soil and, stored in the plants. This is carbon sequestration and the soil is known as a carbon sink.
What is soil?
Soils are naturally made up of four different components, a typical soil consists of:
50% Mineral
20-25% Water
20-25% Air
1 to 12% Organic matter
Obviously, the specific percentages will vary from one soil to another and whether or not it is in wet or dry conditions for example. In winter soils will contain more water than in the summer. The organic matter is made up from all the living and dead material: bacteria, plant roots, dead leaf litter and animal manure for example. This organic matter is full of carbon that is locked in the soil. Different soils will have different soil organic matter (SOM) contents and therefore different carbon contents. For example, a sandy soil will have a low SOM of around 1%, where as a peat-based soil will be at the top end, with clay soils somewhere in between.
A bit of soil history
Around 10,000 years ago man evolved from being a hunter gatherer to a farmer as they started growing crops and grazing animals. They managed the soils, changing the natural habitat to one more favourable to their needs. Right from the first farmers, man has not been very successful at looking after our soils. In fact, every empire in human history has eventually failed due to starvation, mainly bought about by soil degradation. From the Roman Empire, to the more recent collapse of the Soviet Union.
President Franklin Roosevelt once stated, “A nation that destroys its soil, destroys itself.” Wise words indeed, based on thousands of years of proof. However, when Roosevelt made this statement, he was probably thinking of the dust bowls in the mid-west of the American prairies and the loss of the natural habitat caused by farmers ploughing up their land to grow crops. He was very aware of the nutritious soil literally being blown away and was no doubt aware that unless farming practices changed, in time this land would not be able to produce food. But he was probably not aware that the general degradation of the soil was also releasing many thousands of tonnes of CO2 into the atmosphere, adding to what we know today as Global Warming.
Traditionally farmers plough the land, a process to turn the soil over to create good conditions in which to plant the following crop or pasture. However, when the soil is moved intensely as it is in ploughing, the carbon that is locked into that soil is suddenly exposed to our oxygen-rich atmosphere, resulting in the carbon combining with the oxygen to make carbon dioxide, which is released into the atmosphere. At this point the soil changes from being a carbon sink (removing CO2 from the atmosphere) to become a carbon source (releasing CO2 into the atmosphere). Over a few short decades, soils will lose their carbon content and thus reduce the soil organic matter, not only releasing global warming CO2, but also making the soil less nutritious and resilient to extreme weather conditions, which is not good for the farmer.
How are we improving our soils on Bottom Farm?
There is a better way we can grow our crops and graze our animals, using sustainable practises carried out by the likes of LEAF farmers (Linking Environment And Farming). These sustainable farming practises have three crucial but simple requirements to make soils healthy:
– Reduce soil disturbance from intensive cultivation and ploughing
– Keep something growing in the soil all year
– Vary the crops and livestock grown on the soil
By reducing cultivation, and especially ploughing of the soil, the loss of CO2 is greatly reduced. By keeping something growing in the soil as long as possible, not only are the plants utilising the power of the sun, photosynthesising and actively absorbing CO2 from the atmosphere, but the roots are feeding all the microbes in the soil to keep a healthy biodiversity. Finally, by varying the crops and livestock grown on the soil, the farmer better mimics what would happen in nature keeping the soil in good health.
If farmers follow these simple principles, they can again turn the soil back into a carbon sink, sequestering carbon in the soil and increasing the soil organic matter. I have done this on our farm over the last two decades and on one field which I have been monitoring, I have increased the soil organic matter from 3.8% to 6.3% between 2002 and 2016. To put this into context, if every farmer around the world practiced sustainable soil principles, our soils have the ability to remove 1 trillion tonnes of CO2 from the atmosphere, taking us back to pre-industrial levels. So, the prize is extremely big and very worthwhile aiming for.
On the 8th August, we took part in 24 Hours in Farming, the agricultural industry’s biggest online event, which highlights the pride of the nation’s food producers and encourages farmers to show the general public a typical working day through the power of social media using the hashtag #Farm24. Starting at 5am on Thursday 8th and finishing at 5am on Friday 9th, this 24 hour event encouraged British farmers to share an insight into their day to show consumers the effort and care that goes into producing their food.

Duncan Farrington ready for #Farm24
Starting first thing in the morning, Duncan had to move all the barley in the barn back as far as possible, to give plenty of room for the barley he was due to the harvest throughout the day.

View from inside the combine harvester
Meanwhile, Robert (Duncan’s father) and Marvin (our farm worker) started preparing the combine harvester. This involved cleaning the windscreen, blowing the dust from the combine to reduce fire risk, setting up the GPS and getting the combine ready for a busy day. Once everything was set, Marvin starting combining. We use GPS to pinpoint our location in the field and steer the combine through the field, ensuring that each length of the field is harvested as efficiently as possible, reducing fuel usage and taking less time.
We were harvesting spring barley on this particular day. This year our spring barley was destined to be made into malt for beer, so a fairly important crop in our opinion!

Barley being unloaded into the trailer
Whilst Marvin drove the combine, Duncan and Robert took it in turns to fill a trailer load of harvested barley from the combine and take it back to the farm yard and tip it into the barn. By having both Duncan and Robert do this, they were able to keep up with the speed Marvin was harvesting at so the combine didn’t have to stop at any point.

Cover crop seeds – buckwheat & phacelia
We visited another field on Bottom Farm, this one was harvested a few days previously and then planted with cover crops. We use cover crops to improve the health of our soil, but the key benefit is the fact that they absorb CO2 from the atmosphere and store the carbon in the soil (more info here). We planted buckwheat (the bigger, pyramid shaped seeds) which scavenge for phosphate and helps young plants’ root development. We also planted phacelia (the tiny seeds) which have fibrous roots for soil structure. On the same day as #Farm24, the UN also released their latest climate change report, which highlighted the importance of soil and storing carbon from the atmosphere in soil, which is exactly what our cover crops do!
Whilst Duncan was busy with harvest, his wife Eli jumped in a tractor and rolled the fields of cover crops. Rolling smooths the field and ensures the seeds are pushed into a good soil base to give them the best chance for growing.

Eli Farrington in tractor
Next, we headed over to the Mellow Yellow production barn. Mellow Yellow Rapeseed Oil is grown, pressed and bottled on the farm. First of all, the seeds go into big yellow hoppers which feeds the seed into the presses. The seed is then cold pressed which involves being gently squeezed until the yellow oil is released. The seed husk is not wasted, it is shaped into pellets and sold to local farmers as high quality animal feed for cattle, pigs and sheep.

Rapemeal

Rapeseed oil dripping from press
Once the seed has been pressed, the oil trickles out and is simply passed through a filter, a bit like coffee paper, before it is put into bottles. These bottles were then destined for Morrisons, the sponsors of 24 Hours in Farming, a lovely coincidence!
Returning back to the combine harvester, Duncan, Robert and Marvin had lots of barley to harvest, so ended up going until half 10 that night, it’s a good thing the combine has headlights! By the end of the day, we had managed to harvest all the barley, which we were VERY pleased with, especially as rain started to fall the minute after we had shut the combine into the barn, perfect timing or what! The weather often causes problems around harvest, the crops may be ready but if it’s raining, we can’t combine as the moisture levels must be low.

Duncan, Robert and Marvin after a busy day’s harvesting
Throughout the day, hundreds and thousands of British farmers and food producers shared images and videos from their day with #Farm24. It was a fantastic day for learning about how our food is produced. #Farm24 was trending for most of the day and over 8 million people saw the photos and videos shared throughout the day! For more information on 24 Hours in Farming, please visit Farmer’s Guardian here: https://www.fginsight.com/24hoursinfarming/sponsored—24hoursinfarming
Bottom Farm is an arable farm, in other words, we grow crops and not animals. However, when giving talks on sustainable agriculture, I sometimes say that we do have livestock on Bottom Farm in the form of worms, pollinating insects, beetles and a whole host of other beneficial little creepy crawlies that help me grow my crops. They help by recycling old plant debris to create plant food for the growing crops in the case of worms; or pollinating our rapeseed and beans in the case of pollinating insects; or indeed helping with my pest control, in the case of the beetles that eat unwanted aphids on the crops. But in the more traditional sense, we don’t usually have livestock on the farm.
As part of a good sustainable farming system, I grow a healthy rotation of different crops around the farm each year. The basis of this being that different crops take different things from the soil and put different things back. In addition to growing different crop types, we also plant crops at different times of the year which helps in breaking weed and disease cycles. Generally, we plant crops in either the autumn or the spring.
Before planting a spring crop of say, barley, I plant a cover crop in the autumn. A cover crop does just as it says, it covers the ground, protecting the soil from winter rains. By growing a crop throughout the winter months means the growing roots are holding onto precious minerals rather than being washed away in the rainfall. The roots also keep the soil in good structural condition, keeping it lovely and friable for the following spring crop. Finally, the growing crops provide a food source for all those little creepy crawly animals and bacteria in the soil that work altogether to make a healthy fertile soil.
I have tried several different crops over the years and currently favour a mixture of crop species, this includes oats, vetch, phacelia and buckwheat for example, each adding their own little bit of magic to the mix. Generally, I plant the cover crops in August or September and allow them to grow until January or February. As soon as the weather conditions allow, we will apply a herbicide to the crop to kill it off, giving it time to die and breakdown in readiness for the spring barley to be planted in March or April. By giving time for the crop to breakdown, all the bugs in the soil will start converting some of the plant material into nutrition ready for the new planted barley to feed on and grow healthily into a crop to be harvested.
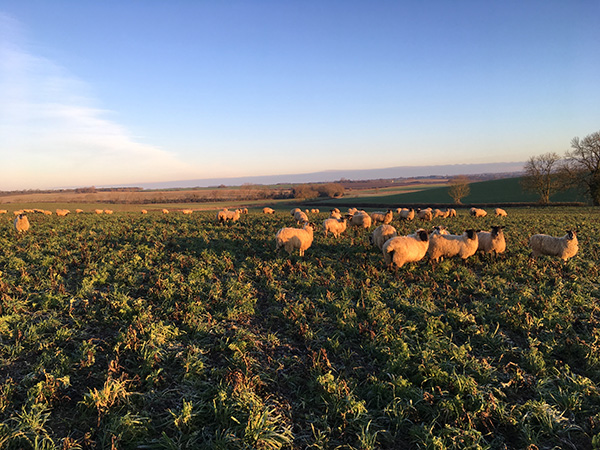

However, let’s return to the topic of livestock on Bottom Farm! Over the last few years, on some of the cover crop fields I have used sheep to graze off the vegetation in readiness to plant the following crop. This traditional method of destroying the cover crop is sometimes called the ‘golden hoof’, as the sheep not only remove the crop, but in the process, convert it into a fresh source of manure, thereby fertilising the soil. The sheep are not mine, but belong to a local farmer who takes them from farm to farm, where he gets good quality grazing for his flock, whilst providing us with an excellent lawnmower and fertiliser service. It does mean for a few weeks a year, I become a livestock farmer and we have sheep on Bottom Farm. I thoroughly enjoy walking the field every morning to check they are all still there and happily grazing. You could say it makes me feel like a real farmer, using traditional methods in our very modern world.
You can learn more about our sustainable farming practises here.

Duncan Farrington
“A nation that destroys its soils destroys itself”
Franklin D Roosevelt.
As a farmer, I have always known that everything I produce is dependent on the soil I grow my crops in and the rain that falls on them. Without these natural resources, we would fail. However, it is not just farmers that soils are important to. They are the cornerstone for the survival of life on earth and, as former American President Roosevelt appreciated, the key to the prosperity of whole nations and civilizations.
Ever since mankind turned from hunter gatherer to farmer, we have had the sad record of destroying our soils, which led to the demise of empires. Whether this being the Ancient Greeks, where ancient monuments are now surrounded by arid bedrock, in what was once fertile farm land. Or the fall of the Roman Empire, which spread out north and south from Italy, in the attempt to bring food in from new agricultural lands. Or more recently the fall of the Soviet Union, as the population got fed up with constantly queuing for essential staple foods, where in reality they were not producing enough food to feed themselves.
In nature crops and animals grow naturally quite well, but they are a bit randomly spread out. As mankind started to domesticate crops and animals for their needs, they started clearing areas of land to produce more food in a given area. The land was cultivated by the plough, originally a small implement pulled by an ox or donkey, today it is much larger and pulled by tractors. But the principle is the same. The plough turns over and breaks up the soil surface to create a seed bed to plant crops in. The advantages are that it provides soils free from weeds, provides good conditions and soil structure for plants to grow in. It also gives a nutritional boost to the plants as bacteria breakdown minerals for the plants to feed off.
Over time the disadvantages of ploughing however outweigh the advantages. The freshly disturbed surface of the earth is very fragile, especially when it rains, with soil erosion being particularly noticeable on slopes. As rain drops hit the soil surface, water drains down-hill into streams, rivers and eventually into seas and oceans. But the water takes the fertile soil particles with them, which in time can remove the soil completely; think of those ancient Greek monuments standing on top of rocky outcrops. But it still happens today as this satellite image of the UK clearly shows. Now whilst I am all for us exporting more products to our friends in Europe, I am not sure we want to be sending them our fertile soil.

This satellite image, taken on 16 February 2014, shows how soil is washed off our fields and out into the sea. ©NEODAAS/University of Dundee
Also, whilst ploughing creates a lovely loose structure for seeds to germinate in, the action of ploughing exposes the soil to oxygen in the atmosphere. This gets all the soil bacteria really excited, similar to a young child being given sugary sweets, running around really quickly, before collapsing in a heap on the floor once the sugar rush is over. The bacteria ‘run around’ in this high oxygen atmosphere, giving lots of nutrition to the crop, but it is short lived as the bacteria eat up the store of carbon in the soil, respiring as they do so, and thus release the stored carbon to the atmosphere as carbon dioxide. This has the double negative effect, of gradually reducing the nutritional content of the soil and increasing the global warming effects of increased CO2 in the atmosphere.
Having learnt much on soil quality over the years, I took the decision not to plough on our farm back in 1998. Admittedly, my incentive was not just to save the planet, but also to save money as ploughing is an expensive operation. Although it was known my crop yields could reduce a little, hopefully this would be more than compensated by reduced costs. When I stopped ploughing, I made lots of mistakes as yields reduced dramatically for a short period, as well as weed pressure increasing. Our neighbours thought I was a bit daft – they may be right on that one. But over the years, I have learnt an awful lot as the system has improved. The theory of not ploughing is that naturally plant roots and creatures like worms improve soil structure. The bacteria and other micro fauna improve the soil health and biology, converting old plant residues and mineral content of the soil into plant food. So by not ploughing, the soil structure and organic matter content gradually improves year on year and, the carbon from the soil is not released to the atmosphere as CO2. I continue to learn from my experiences as we are making a healthy environment for the plants to grow in, but this is the underlying theory.
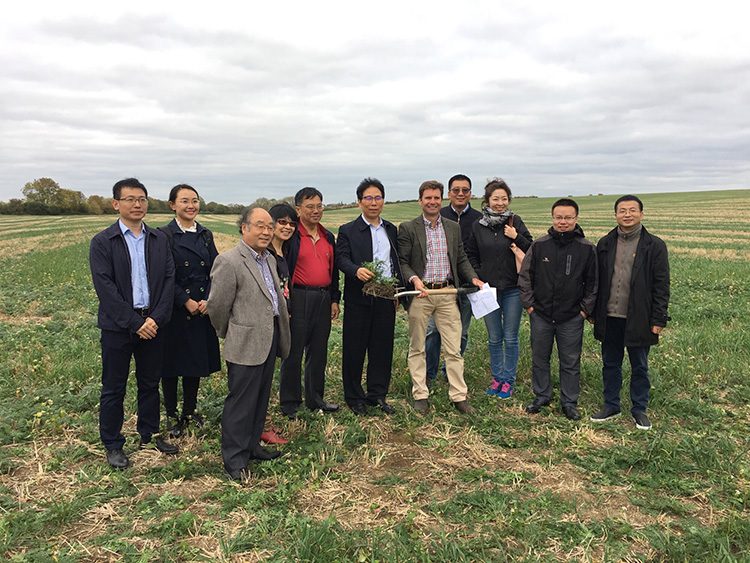

Delegation from China, including Deputy Director General of the Ministry of Agriculture and the Chinese delegate for the United Nations Environment team.
Today, soil health is something that governments around the world are realising is important and we should be doing something to improve our most important natural asset. I was especially proud recently when, along with LEAF, I hosted a delegation from China which included; The Deputy Director General of the Ministry of Agriculture and the Chinese delegate for the United Nations Environment team. They were very interested in what we are achieving with our soil health on the farm.
Plenty of commentators accuse agriculture of being a huge cause of global warming from CO2 emissions, however I can show from what we are doing on our farm, agriculture can play a major role in reducing CO2 emissions when looking after our soils.
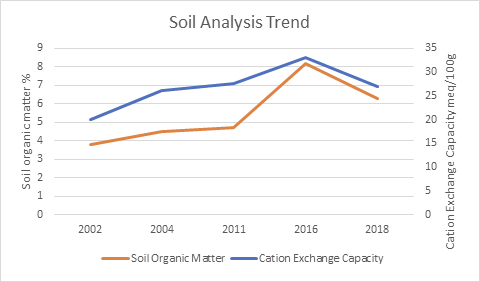
Below Black Barn field, Bottom Farm
The graph shows how the soil on our fields is improving in quality, by increasing in soil organic matter. To put this another way, we are actively absorbing CO2 out of the atmosphere and locking it into our soils. If this is repeated around the world, the benefits could be enormous; it has been estimated that agriculture could reduce global CO2 emissions by between 10% to potentially 30%. The graph also shows the increase in Cation Exchange Capacity (C.E.C). In basic terms as the CEC increases, there is more nutrition within the soil for the plants to grow healthily.
So, in the space of a few years of trying to work with nature, the results clearly show we are creating a healthier, more nutritious environment for crops to grow in. Not only is this good for the soil and the wider environment, but it is good for us also, as healthy soils grow healthy crops and healthy crops create healthy food for us to enjoy eating.
Learn more about our environmental credentials here and where to buy our LEAF Marque Cold Pressed Rapeseed Oil here.
After several years of trying, I am excited to report that renewable energy has returned to Bottom Farm!
As a family we have always been environmentally aware and energy efficient even if, originally, we didn’t realise it. Let me explain. Most actions we take as a society to become more energy efficient are driven nowadays by doing the right thing for the environment and for future generations. In my mind this is the right thing to do. However, these actions are also good common sense and a great way to save a bit of money.
Many years ago, my pioneering Grandfather became one of the first people in Britain to generate electricity from a windmill for his home, see the timeline on our website showing this. He also built his own solar panels to heat water, so he could have a hot bath in the evenings. Later, my Father made his own central heating boiler to burn waste timber from the local timber yard to heat our house. I remember as a teenager in school holidays, having to fill and light the boiler every morning with six-foot lengths of off-cut pine, leftover from the manufacture of garden sheds and fences. Without this boiler, we wouldn’t have hot water, or a warm house.
Today such practices would be applauded as great examples of people doing their bit for the environment. However, the reality was that both my Father and Grandfather, were driven by ways to run their homes efficiently in order to save a bit of money. Plus they both enjoyed trying to do things a bit differently. Eventually the timber yard closed down and the boiler was at the end of its life, so it was replaced with a modern oil-fired central heating boiler.

Duncan’s grandfather’s home-built windmill
Move forward a few years and people became more aware of our effect on the environment and potential ways to ‘reduce one’s carbon footprint’ by creating ‘renewable energy’ using a whole range of new and exciting technologies such as: solar photo voltaic systems; biomass boilers or combined heat and power; ground source heat pumps; rain water harvesting and several more. We have collected rain water both on the farm and at our home for many years. Our youngest daughter, Amelia, was talking about this in her geography class only the other day, not realising that this is still relatively unusual, as she assumed this was standard in all homes and couldn’t understand why not.
Apart from rainwater harvesting and other good practises like using LED lighting, or even encouraging people to turn lights off, or to keep doors closed when it is cold, we have not had any renewable energy at Bottom Farm for over fifteen years. This was not for lack of trying though…
Around the turn of the Millennium, we looked at installing a wind farm on the farm. I was keen to follow in my Grandfather’s footsteps and thought people would love the idea, but unfortunately our neighbours in the village were not quite as enthusiastic as I was. We gave up on that idea soon after. Later, when Farrington Oils needed more electricity, I looked at putting solar panels on the factory roof, however it turned out that as we live in a small village, with Bottom Farm being at the end of the power line, we had the wrong sort of electricity and not enough of it to work with solar panels. So again, a dead end.

Our grain store, pre-solar panels

Our grain store, during solar panel installation
Now after three years of planning, working with the local electricity supplier and substantial investment on our part, we now have a new electricity supply to Bottom Farm. The local electricity supplier is delighted with this as they can give a more reliable supply to the rest of Hargrave, meaning that lights and televisions will stay on in the winter months. More importantly, it is now the right sort of electricity to work with solar panels!
We now finally have solar panels on two barn roofs, which will generate over half the total electricity we use at Bottom Farm. So, when you enjoy using Mellow Yellow in your cooking, just think, your little bottle of sunshine is grown using the power of the sun and then cold pressed with the power of the sun too. Surely that’s got to be good for all our futures?

Our grain store with completed solar panels
Duncan Farrington

In May this year, when our rapeseed fields were looking their best in full bloom, Nadiya Hussain and a filming crew from Hungry Gap Productions came to Bottom Farm to learn more about how we produce our cold pressed rapeseed oil. The reason for the visit was to film a segment for Nadiya’s new series, Nadiya’s Family Favourites!
Starting in the fields, Duncan explained how he grows the rapeseed to LEAF (Linking Environment and Farming) Marque standards and how the plant grows. He then showed Nadiya the cold pressing method we use and how we bottle our oil.
As Nadiya is obviously a brilliant baker and chef (she won the Great British Bake Off in 2015) she was keen to learn more about cooking with Mellow Yellow Cold Pressed Rapeseed Oil! So she headed off to The Mermaid in Ellington and head chef, Nick Marriot put her taste buds to the test with a roast potato challenge. After cooking roast potatoes in either cold pressed rapeseed oil, sunflower oil or olive oil, Nick challenged Nadiya to identify each oil. With it’s high smoke point giving super crispy roasties and subtle nutty flavour, she easily spotted the ones cooked in Mellow Yellow!
We absolutely loved having Nadiya visit us at Bottom Farm, it was a fantastic day and watching ourselves on TV is incredibly exciting! If you didn’t catch the episode live last week, you can catch up on BBC iPlayer now: https://www.bbc.co.uk/iplayer/episode/b0bc26qk/nadiyas-family-favourites-series-1-1-family-days-out
Nadiya’s Family Favourites is on BBC2 every Monday at 8pm.

 Oils
Oils Rapeseed Oil
Rapeseed Oil Chili Oil
Chili Oil Dressings
Dressings Blackberry Vinaigrette
Blackberry Vinaigrette Classic Vinaigrette
Classic Vinaigrette Balsamic Dressing
Balsamic Dressing Honey & Mustard
Honey & Mustard Ultimate Chilli Dressing
Ultimate Chilli Dressing